About MiraLAX®
About MiraLAX®


Experts recommend starting with MiraLAX® first for treatment of occasional constipation (OC)1-3
Experts recommend starting with MiraLAX® first for treatment of occasional constipation (OC)1-3
Dr. Darren Brenner starts with MiraLAX® for the treatment of OC for his patients. Watch his video to see why.
Watch Dr. Darren M. Brenner present his approach to patient care and his views based upon updated systematic review data and consensus statements1-3
Watch Dr. Darren M. Brenner present his approach to patient care and his views based upon updated systematic review data and consensus statements1-3
Darren M. Brenner
MD, FACG, AGAF, RFF
Professor of Medicine and Surgery, Director—Northwestern Neurogastromotility Program, Northwestern University—Feinberg School of Medicine
Dr. Brenner, a Bayer consultant, has received compensation from Bayer for his participation in this video.
Click to expand.
References: 1. Brenner DM, Corsetti M, Drossman D, Tack J, Wald A. Perceptions, definitions, and therapeutic interventions for occasional constipation: a Rome Working Group consensus document. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;22(2):397-412. doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2023.08.044 2. Rao SSC, Brenner DM. Efficacy and safety of over-the-counter therapies for chronic constipation: an updated systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(6):1156-1181. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000001222 3. Rao SSC, Brenner DM. Evidence-based treatment recommendations for OTC management of chronic constipation. J Am Assoc Nurse Pract. 2022;34(9):1041-1044. doi:10.1097/JXX.0000000000000760
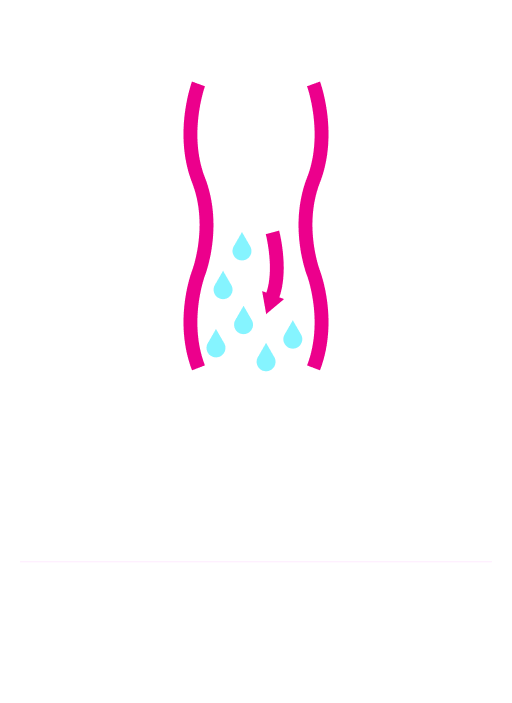
MiraLAX® has a triple mechanism of action that hydrates, softens, and gently relieves1-3
MiraLAX® has a triple mechanism of action that hydrates, softens, and gently relieves1-3
The triple action of MiraLAX®
The triple action of MiraLAX® provides proven results and a comfortable patient experience
MiraLAX® triggers peristalsis without interacting with bacteria6 or causing nerve stimulation,2 which can lead to harsh side effects.
MiraLAX®
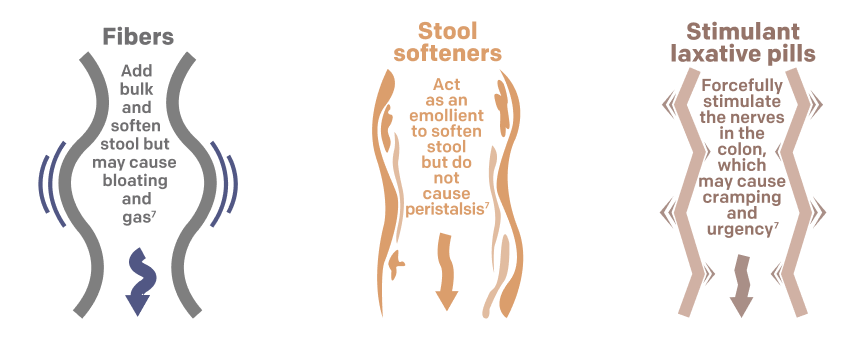
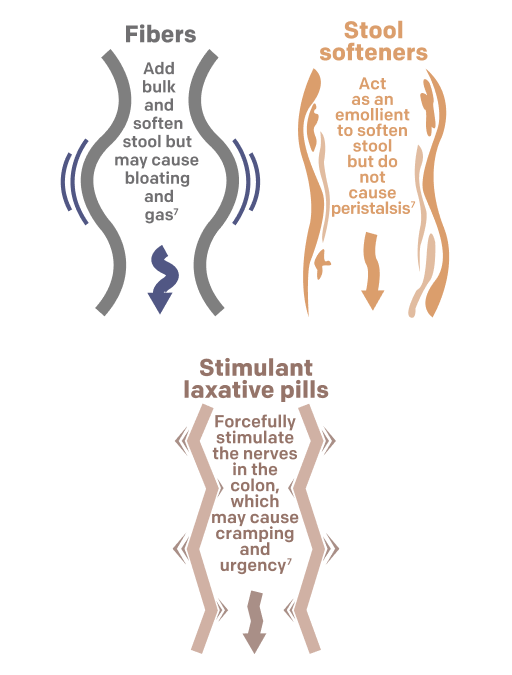
- Doesn’t metabolize in the intestine, which could cause bloating and gas buildup as with fibers such as Metamucil®6,7
- Encourages gentle peristalsis, unlike stool softeners such as Colace®, which do not prompt peristalsis and could cause cramps and diarrhea7
- Doesn’t forcefully stimulate colonic nerves, which could cause stomach discomfort and cramps, as with stimulant laxatives such as Dulcolax®7
The trademarks mentioned herein are owned by their respective owners.
See how MiraLAX® works in the body
MiraLAX®: Its triple mechanism of action relieves constipation without causing bloating, cramping, gas, or urgency4-6
Compare how MiraLAX® and other constipation options work
MiraLAX®: Its triple mechanism of action relieves constipation without causing bloating, cramping, gas, or urgency4-6
Compare how MiraLAX® and other constipation options work

In multiple clinical trials, MiraLAX® has been proven to
In multiple clinical trials, MiraLAX® has been proven to
MiraLAX® is the ONLY OTC osmotic laxative with a prescription heritage and is favored by both physicians and patients10,11
MiraLAX® is the ONLY OTC osmotic laxative with a prescription heritage and is favored by both physicians and patients10,11
MiraLAX® is supported by over 25 years of safe and effective use. It was FDA approved in 1999 as an RX, and as an OTC product in 200612,13
MiraLAX® provides predictable and reliable relief for a broad range of patients5,8,15
MiraLAX® provides predictable and reliable relief for a broad range of patients5,8,15

MiraLAX® is available in a variety of dosing sizes, including travel-size packets
MiraLAX® is available in a variety of dosing sizes, including travel-size packets
MiraLAX® is easily accessible at national drug store chains, mass merchandisers, online retailers, and club stores
Start your patients on triple-action MiraLAX®
Start your patients on triple-action MiraLAX®
Click to expand.
References: 1. Schiller LR, Emmett M, Santa Ana CA, Fordtran JS. Osmotic effects of polyethylene glycol. Gastroenterology. 1988;94(4):933-941. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(88)90550-1 2. Hammer HF, Santa Ana CA, Schiller LR, Fordtran JS. Studies of osmotic diarrhea induced in normal subjects by ingestion of polyethylene glycol and lactulose. J Clin Invest. 1989;84(4):1056-1062. doi:10.1172/JCI114267 3. Andrews CN, Storr M. The pathophysiology of chronic constipation. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011;25(Suppl B):16B-21B. 4. DiPalma JA, DeRidder PH, Orlando RC, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter study of the safety and efficacy of a new polyethylene glycol laxative. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95(2):446-450. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.01765.x 5. DiPalma JA, Cleveland MB, McGowan J, Herrera JL. A comparison of polyethylene glycol laxative and placebo for relief of constipation from constipating medications. South Med J. 2007;100(11):1085-1090. doi:10.1097/ SMJ.0b013e318157ec8f 6. Hammer HF, Hammer J, Gasche C. [Polyethylene glycol (Macrogol)—an overview of its use in diagnosis and therapy of gastrointestinal diseases]. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2000;112(2):53-60. 7. Fiorini K, Sato S, Schlachta CM, Alkhamesi NA. A comparative review of common laxatives in the treatment of constipation. Minerva Chir. 2017;72(3):265-273. doi:10.23736/S0026-4733.17.07236-4 8. MiraLAX® Drug Facts. 9. Cleveland MvB, Flavin DP, Ruben RA, Epstein RM, Clark GE. New polyethylene glycol laxative for treatment of constipation in adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. South Med J. 2001;94(5):478-481. 10. Bharucha AE, Dorn SD, Lembo A, Pressman A. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement on constipation. Gastroenterology. 2013;144(1):211-217. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.10.029 11. Data on file. Bayer Healthcare. 12. US Food and Drug Administration. NDA 20-698. Approval letter for MiraLAX powder. February 18, 1999. 13. US Food and Drug Administration. NDA 22-015. Approval letter for MiraLAX powder OTC. October 6, 2006. 14. Pharmacy Times. 2024 survey of pharmacists’ OTC recommendations: OTC guide. Accessed October 3, 2024. https://www.pharmacytimes.com/publications/otc 15. DiPalma JA, Cleveland MvB, McGowan J, Herrera JL. A randomized, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial of polyethylene glycol laxative for chronic treatment of chronic constipation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:1436-1441. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01199.x









